_5.jpg is missing or invalid' in D:\Sites\pc-web\assets\vendors\filemanager\include\php_image_magician_custom.php:120:5
Stack trace:
#0 D:\Sites\pc-web\assets\vendors\filemanager\include\utils.php(294,3): imageLib->resizeImage
#1 D:\Sites\pc-web\assets\vendors\filemanager\upload.php(95,9): create_img
#2 {main}.<br/>
)

C: capacitance value
Generally, it is measured at 1 kHz, 1V equivalent AC voltage, DC bias is 0V, but there are many environments where capacitance measurement is different. However, it should be noted that the capacitance value C itself will change with the environment.
ESL: Capacitance equivalent series inductance
The pin of the capacitor is inductive. Insensitive to low frequency applications, so it can be ignored. When the frequency is high, consider this inductor. For example, a 0.1uF chip capacitor in a 0805 package has a 1.2nH inductance per pin. The ESL is 2.4nH. It can be calculated that the resonant frequency of C and ESL is about 10MHz. When the frequency is higher than 10MHz, the capacitance is Inductive characteristics.
ESR: Capacitance equivalent series resistance
No matter which capacitor has an equivalent series resistance, when the capacitor operates at the resonance frequency, the capacitive reactance and inductance are equal, so it is equivalent to a resistor . This resistor is ESR. There are big differences due to different capacitor structures. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors ESR generally range from a few hundred milliohms to several ohms, ceramic capacitors are typically tens of milliohms, and tantalum capacitors are between aluminum electrolytic capacitors and ceramic capacitors.
Of course, there are many capacitor-related parameters, but the most important ones in the design are C and ESR. The following briefly introduces the three capacitors we commonly use: aluminum electrolytic capacitors, ceramic capacitors and tantalum capacitors.
1) The aluminum capacitor is made by etching the aluminum foil groove and then engraving the insulating layer, and then dip the electrolyte solution. The principle is chemical principle. The capacitor charge and discharge depends on the chemical reaction, and the response speed of the capacitor to the signal is affected by the electrolyte. The moving speed limit of the charged ions in the medium is generally applied to the filtering of the lower frequency (below 1M). The ESR is mainly the sum of the equivalent resistance of the aluminum crucible and the electrolyte, and the value is relatively large.
The electrolyte of the aluminum capacitor will gradually evaporate, resulting in a decrease or even a failure of the capacitor, and the evaporation rate will increase as the temperature increases. For every 10 degrees increase in temperature, the life of the electrolytic capacitor is halved. If the capacitor can be used for 10,000 hours at room temperature of 27 degrees, only 1250 hours can be used in a 57 degree environment. Therefore, the aluminum electrolytic capacitor should not be too close to the heat source.
2) The storage of the ceramic capacitor is based on the physical reaction, so it has a high response speed and can be applied to the upper G. However, the ceramic capacitors vary greatly depending on the medium. The best performance is the capacitor of C0G material, the temperature coefficient is small, but the dielectric constant of the material is small, so the capacitance cannot be made too large.
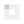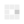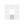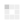
The worst performance is the Z5U/Y5V material. This material has a large dielectric constant, so the capacitance can be tens of microfarads. However, this material is affected by temperature and DC bias (DC voltage will cause the material to be polarized, resulting in reduced capacitance). Let us look at the C0G, X5R, Y5V three material capacitors affected by the ambient temperature and DC operating voltage.

.jpg)
It can be seen that the capacitance of C0G does not change with temperature, and the stability of X5R is slightly worse. When the material of Y5V is 60 degrees, the capacity becomes 50% of the nominal value.
.jpg)
It can be seen that the 50V withstand voltage Y5V ceramic capacitor has a capacity of only 30% of the nominal value when applied at 30V. Ceramic capacitors have a big drawback, which is fragile. So you need to avoid bumps and try to stay away from the board where the deformation is easy.
3) Tantalum capacitors are like a battery in principle and structure. The following is a schematic diagram of the internal structure of the tantalum capacitor:
.jpg)
Tantalum capacitors have the advantages of small size, large capacity, fast speed, low ESR, and high price. The size of the tantalum capacitor and the pressure resistance are determined by the size of the raw material powder particles. The finer the particles, the larger the capacitance, and the thicker the Ta2O5 if a larger pressure is required, which requires the use of larger particles of tantalum. Therefore, it is very difficult to obtain a tantalum capacitor with a high withstand voltage and a large capacity.
Another place where tantalum capacitors need attention is that tantalum capacitors are easier to break down and have short-circuit characteristics, and have poor surge resistance. It is very likely that a short circuit is caused by a large instantaneous current causing the capacitor to burn out. This should be considered when using ultra-capacitance tantalum capacitors (such as 1000uF tantalum capacitors).
It can be seen from the above that different capacitors have different applications, and the higher the price, the better.