I. Overview of Ignition Coil
What is an Ignition Coil?
An ignition coil is a critical component in the operation of an engine, providing power for the ignition process to ignite the compressed fuel mixture. In essence, it is a transformer that converts the low voltage electrical current from the vehicle into high-voltage electricity required for sparking the spark plugs. The primary function of an ignition coil is to generate high-voltage pulses and transfer electrical energy to the spark plugs, thereby igniting the air-fuel mixture. It provides the high voltage necessary for the ignition system to ensure reliable ignition and combustion. Typically, each cylinder is equipped with an ignition coil and spark plug set, with most ignition coils requiring replacement after approximately 100,000 kilometers or even longer.
Working Principle and Structure of Ignition Coil
The working principle of an ignition coil is based on the electromagnetic induction principle of an electromagnetic component. This component consists of a engine coil with two ends connected to two switches, with one end initially at a low voltage and the other end having the same voltage as the power supply. When the two switches on the low voltage end are respectively connected to the engine power supply and the control circuit of the signal lamp, the rise in power supply voltage causes electromagnetic induction within the coil, resulting in an increase in voltage at the other end of the coil. An ignition coil comprises several main parts, including the primary coil, secondary coil, iron core, and switch mechanism.
The ignition coil diagram often illustrates the layout of the primary and secondary coils surrounding an iron core. The primary coil is typically a thicker coil responsible for generating the initial magnetic field, while the secondary coil consists of thinner coils used to produce higher voltage.
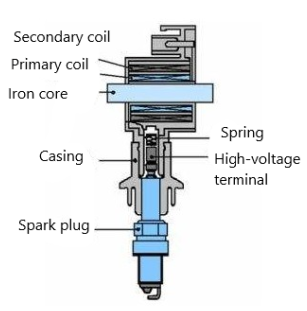
Ignition coil diagram
How long do ignition coils last?
The lifespan of ignition coils can vary depending on various factors such as the quality of the coil, driving conditions, maintenance practices, and the specific vehicle model. On average, ignition coils are expected to last between 80,000 and 100,000 miles (128,000 to 160,000 kilometers).
Regular maintenance practices such as keeping the ignition system clean, replacing spark plugs at recommended intervals, and addressing any underlying issues promptly can help extend the lifespan of ignition coils. Additionally, using high-quality ignition coils and following manufacturer guidelines for maintenance can also contribute to their longevity.
II. Symptoms of a bad ignition coil
Firstly, when an ignition coil fails, the most common symptom is the engine's inability to start or difficulty in starting. This is because the ignition coil cannot provide sufficient high-voltage electrical energy to the spark plug, resulting in the inability to ignite the fuel mixture. In such cases, the engine may make intermittent starting sounds but fails to continuously run.
Second, another sign of bad ignition coil is that it will cause engine instability. When the ignition coil fails to provide a stable high-voltage electrical energy, the spark plug's ignition performance is compromised, causing the engine to experience shaking, misfires, or other issues during idling or low-speed driving. Additionally, the engine's power output may be weakened, resulting in poor acceleration or sluggishness.
Furthermore, a weak ignition coil can increase fuel consumption. When the ignition coil fails to function properly, the spark plug's ignition efficiency is reduced, leading to decreased combustion efficiency and incomplete fuel burning. As a result, fuel consumption is increased. Ignoring this issue for an extended period not only raises the operating costs but also has adverse environmental impacts.
Moreover, a faulty ignition coil can cause the engine to exceed emission standards. Ignition coil malfunctions can result in inadequate spark plug ignition, reduced combustion efficiency, and increased emission of harmful gases. This not only causes pollution to the environment but also may prevent the vehicle from passing emission tests, rendering it unable to legally operate on the road.
III. Solutions for Ignition Coil Malfunctions
Replace the ignition coi in the car: If the ignition coil is severely damaged and cannot be repaired, it needs to be replaced with a new one. During the replacement process, it is important to select an ignition coil that is compatible with the vehicle model and ensure its reliability.
Clean the ignition coil: Sometimes ignition coil malfunctions can be caused by carbon buildup or dust accumulation. You can try using a specialized cleaning agent to clean the ignition coil on the car. After cleaning, the performance of the ignition coil may improve.
Check the power supply: The ignition coil requires a stable power supply to function properly. Therefore, after ruling out other issues, it is necessary to check if the power supply to the ignition coil is normal. If an unstable power supply is detected, timely repair or replacement of the relevant components is required.
Inspect other related components: Ignition coil malfunctions can sometimes be caused by issues with other related components, such as the ignition switch or spark plugs. Therefore, when addressing ignition coil issues, it is important to check if other related components are functioning properly.
IV. The cost of replacing an ignition coil
How often to replace ignition coil
Ignition coils are generally recommended to be replaced every 100,000 kilometers (62,000 miles).
During the operation of an automobile engine, the ignition coil is subjected to high-voltage surges of nearly kilovolts. Due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures, dust, and vibrations, the ignition coil inevitably ages and may become damaged. Failure to replace a faulty ignition coil can adversely affect the engine's performance. However, the recommended replacement interval of 100,000 kilometers is not a fixed timeframe. As long as the ignition coil can function properly and shows no visible signs of aging, it may not require immediate replacement.
An effective method to determine the aging of an ignition coil is to open the engine hood and observe for any signs of leaking resin, explosions, damage to rubber hoses, or pressure nozzle burns. To check if the ignition coil in a vehicle is functioning properly, there is a simple and convenient method: After the vehicle has been running for a while, grasp the ignition coil firmly with your hand. If it can be held without any issues, it indicates normal functioning. However, if it cannot be firmly grasped, it suggests a problem, typically an internal short circuit.
How much to replace ignition coil for cars
Like most automobile parts, the automobile ignition coils on the market will vary in price due to the brand, the original factory/auxiliary factory and other differences, and of course, the value of your vehicle. On average, the cost of replacing a single automotive ignition coil can range from $100 to $400. However, it's important to note that this is just a rough estimate, and the actual cost may be higher or lower depending on the specific circumstances. It's always a good idea to get quotes from multiple mechanics or repair shops to ensure you're getting a fair price.
V. How to test ignition coil
How to test ignition coil with multimeter
- Turn off the engine and disconnect the high-voltage wire between the ignition coil and the spark plug.
- Set the multimeter to the resistance measurement mode (Ω).
- Connect one probe of the multimeter to the terminal of the primary coil of the ignition coil, and connect the other probe to the ignition coil's casing or ground.
- Check the reading on the multimeter. Under normal circumstances, the resistance of the primary coil should fall within the specified range. You can refer to the vehicle's service manual or the ignition coil's specification table to determine the normal resistance value.
Here is an useful video to help you test automotive ignition coils:
How to test ignition coil without multimeter
Note: Without a multimeter, the methods for testing an ignition coil are limited, and it may not provide precise measurement results. If possible, it is recommended to use a multimeter for testing.
- Turn off the engine and disconnect the high-voltage wire between the ignition coil and the spark plug.
- Reconnect the high-voltage wire between the ignition coil and the spark plug.
- Insert an insulated screwdriver or a similar metal tool into the end of the high-voltage wire of the ignition coil, keeping it at a certain distance (approximately 1/4 inch) from the engine ground or metal component.
- Ask someone to help you start the engine and observe if there are visible sparks at the end of the high-voltage wire.
- If you see a bright spark, it indicates that the ignition coil is working properly.
- If there are no sparks or only very weak sparks, it may indicate a problem with the ignition coil.
Please note that there is a risk of electric shock when using a screwdriver or similar tool to test the ignition coil. Ensure that you take appropriate safety precautions and follow the correct operating procedures. It is best to have the ignition coil accurately tested and diagnosed by an experienced professional technician.
Also read: Why is my engine light blinking and how to fix it?