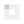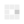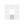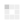
Before we start the comparison of a Power transformer and a distribution transformer it is very important to know what is a transformer? , working principle of transformer, and types of a transformer. A transformer is a device used to transfer electric energy from one AC circuit to one other or more circuits by changing its voltage. It can be either in the form of step-up voltage or step-down voltage where voltage has increased or decreased respectively, Transformer works on the principle of "electromagnetic induction" in which changing current in one coil induces the current into the other coil. Similarly, transfer has a primary coil, in which the magnetic lines build or collapse with the change in current and this current is induced into the secondary coil. We can calculate the secondary voltage by simply multiplying the voltage of the primary coil with the ratio of the number of turns of the secondary coil to the number of turns in the primary coil as given below. This voltage equation ratio will be as follow
Vs/Vp=Ns/Np.
Vs= Secondary Voltage
Vp= Primary Voltage
Ns= No of turn on secondary coil
Np= No of turn on primary coil
Figure 1 Basic Diagram of a Transformer
Types of Transformers:
As far as the types of transformer are concerned the classification of the transformers is based on phase, the functions of the transformers, winding, and core design of the transformers.
- Based on phase the transformers are divided into two categories, single-phase transformerand three-phase transformer.
- Based on the function of the transformer they are categorized into step-up transformer(higher output voltage on secondary coil and step-down transformer (lower output voltage on secondary coil).
- Based on the winding of the transformerwe have two winding transformer which is also known as conventional transformer and auto transformer that contains only one winding.
- If we classify the transformers on the base of the core design of transformerswe will have a Berry-type transformer, Core type transformers, and Shell type transformer.
- According to the usage of transformer, we have isolation transformer, power transformer and distribution transformer and instrument transformerthat we’ll discuss in detail.
Types of transformers on the basis of their purpose:
- Power Transformers
Power transformers have a vital role in the transmission and are mainly used in the transmission of higher voltages. Power transformers make power accessible by transferring electrical energy through transmission lines over long distances. Power transformers are of high rating value transformers.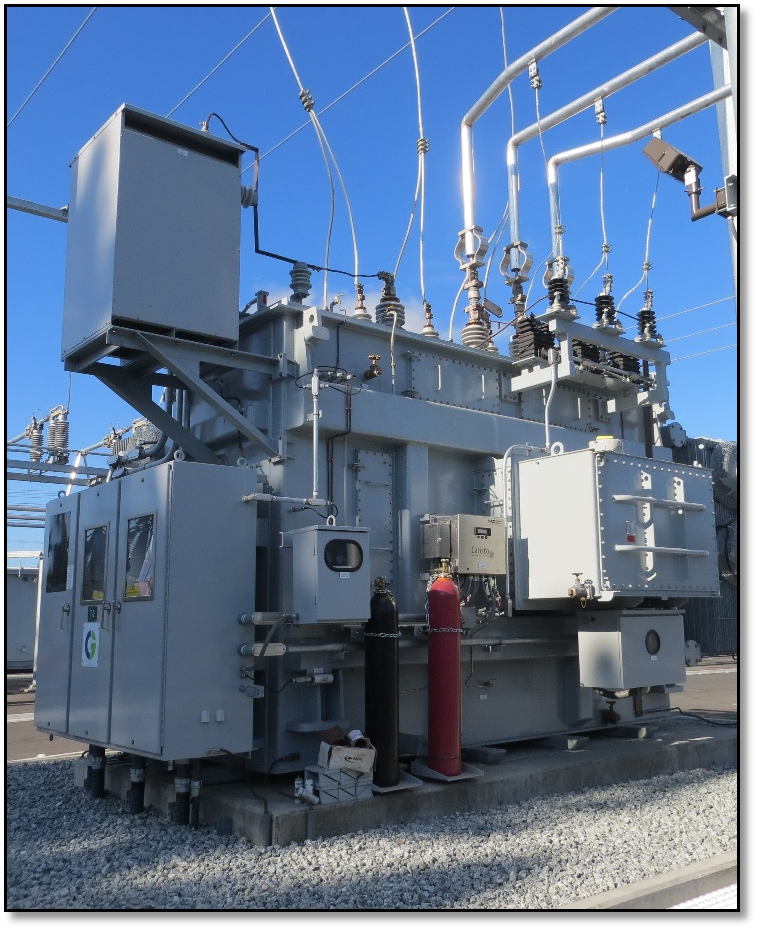
Figure 2 A power transformer installed in substation
- Distribution Transformers
The distribution transformer is like a consumption transformer, provides the vital function of switching from a low-medium voltage source to the voltage used for domestic purposes and commercial use. The distribution transformers are equipped with good voltage regulation.

Figure 3 Distribution transformer on electric pole
Let's discuss the main difference between a power and distribution transformer,
- Ratings:
Power Transformer:
Ratings of transformer varies in different types of transformers, power transformers are mainly used for transmission so have higher ratings ( 400kV, 200kV, 110kV, 66kV, 33kV ) and are rated more than 200MVA.
Distribution Transformers:
On the other hand, distribution transformers are used on the low voltage side and have ratings ( 11kV, 6.6kV, 3.3kV, 440V, and 230V) and rated less than 200MVA.
- Size and Installation Level:
Power transformers:
These transfers are bigger as compared to the distribution transformers because power transformers make transmission possible at heavy loads and higher voltage with 100%. So power transformers are the vital component of power generation and substations.
Distribution transformer:
On the other hand, distribution transformers are lighter than power transformers and easy to install. The distribution transformer is installed on the user end for domestic load and commercial load with a voltage ranging from 440V-220V with a lower efficiency of 50% as compared to the power transformers.
- Losses in transformers:
Power Transformer:
Iron and Copper losses take place in power transformers 24 hours a day. Because the power transformers working in a transmission lines day and night. This is because power transformers are designed in such a way as to maximize efficiency at full load conditions.
Distribution transformers:
In the case of distribution transformers, as they are directly connected to the used end load fluctuations are higher as compared to the distribution transformers where average loads are near to the full load. So in the distribution transformers, Iron losses take place throughout the day and Copper losses are less as compared to the power transformer and depend upon the load cycle.
- Efficiency of transformers:
A power transformer differs from a distribution transformer in its maximum efficiency because a distribution transformer is designed to achieve an efficiency of 60% to 70% a distribution transformer doesn't operate at full load throughout the day on the other hand power transformers are designed to achieve the maximum efficiency of 100% because the work 24 hours a day and play a vital role in the transmission of electrical energy over long distance and being near to electrical grids. Whereas distribution transformers are used on the user end where voltage is much lower as compared to the power transformer and it is not possible to deliver electrical energy over long distances. It's because of voltage drop limitations. This results in the involvement of "clusters of load" in the distribution systems fed from distribution transformers.