In electronic systems, GND is used to receive and transmit electronic signals so that electronic devices can function properly. GND can be used to connect electronic devices, batteries, and power systems to ensure the normal operation of electronic devices. So what is GND? This paper will introduce the definition, function and importance of GND in circuit design in detail.
What is GND in electronics
GND is the abbreviation of Ground, refers to the ground wire, also known as the ground wire. It is a part of electrical equipment used to ground current signals in the metal housing and circuits of electrical equipment. Ground wires can prevent circuit failures caused by leakage and other reasons, and prevent electromagnetic interference caused by the current in the circuit. Ground wires can also connect the metal housing of electrical equipment to the ground point of the power system, thus helping to establish a safe electrical system.
GND is a polarity, it is negative. GND connection point or negative terminal of the device, its current flows from the positive terminal of the power supply to the negative terminal of GND, that is, the negative terminal of GND is the return point of the current. GND can also break up the sparks in the circuit, thus protecting the circuit.
Here are some common symbols for ground wire.
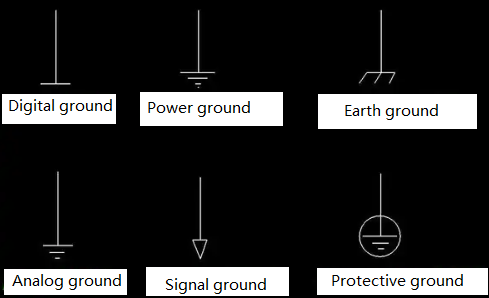
Types of GND wire
A. Power Supply Ground (GND)
The analog ground wire (AGND), digital ground wire (DGND), and power ground wire (PGND) are all classified as DC ground wires (GND). These different types of ground wires ultimately converge as the 0V reference ground wire for the entire circuit, known as the power supply ground (GND). The power supply serves as the energy source for all circuits. The voltage and current required for the operation of any circuit come from the power supply. Therefore, the ground wire (GND) of the power supply serves as the 0V voltage reference point for all circuits. This is why other types of ground wires, whether it's the analog ground wire (AGND), digital ground wire (DGND), or power ground wire (PGND), all need to converge with the power supply ground (GND).
B. Power Ground (PGND)
Whether it's the analog ground wire (AGND) or the digital ground wire (DGND), they are both used in low-power circuits. However, in high-power circuits such as motor drive circuits or solenoid drive circuits, there is a separate reference ground wire known as the power ground (PGND). High-power circuits, as the name suggests, involve higher current levels. It is evident that high currents can cause ground offset between different functional circuits. Once there is a ground offset in the circuit, the original 5V voltage may no longer be 5V but could become 4V. This is because the 5V voltage is referenced to the 0V of the ground wire (GND). If the ground offset causes the GND to shift from 0V to 1V, the previous 5V (5V - 0V = 5V) voltage becomes the current 4V (5V - 1V = 4V).
C. Digital Ground (DGND)
The digital ground wire (DGND) is primarily used in the digital circuit portion, in contrast to the analog ground wire (AGND). It is commonly employed in circuits such as keypad detection circuits, USB communication circuits, and microcontroller circuits. The establishment of the digital ground wire (DGND) is due to the common characteristic of digital circuits, which are discrete binary signals distinguished by "0" and "1". During the transition from a "0" voltage to a "1" voltage or vice versa, there is a voltage change. According to Maxwell's electromagnetic theory, a changing current produces a magnetic field in its surroundings, resulting in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) radiation to other circuits. To mitigate the impact of EMC radiation on the circuit, a separate digital ground wire (DGND) is used to provide effective isolation for other circuits.
D. Analog ground (AGND)
The analog ground wire (AGND) is primarily used in the analog circuit section, such as the ADC acquisition circuit for analog sensors and operational amplifier circuits. In these analog circuits, since the signals are analog and typically weak, they are susceptible to the influence of high currents from other circuits. Without proper differentiation, high currents can create significant voltage drops in the analog circuit, leading to signal distortion and potentially causing malfunctioning of the analog circuit.
E. AC ground (CGND)
AC ground (CGND) is typically found in circuits that involve AC power sources, such as AC-DC power supply circuits. AC-DC power supply circuits are divided into two sections. The front-end of the circuit is the AC section, while the back-end is the DC section. This configuration necessitates the presence of two ground wires: the AC ground and the DC ground. The AC ground serves as the 0V reference point for the AC circuit section, while the DC ground serves as the 0V reference point for the DC circuit section. To unify the ground in the circuit, engineers often connect the AC ground to the DC ground using a coupling capacitor or inductor.
F. Earth ground (EGND)
The safe voltage for the human body is below 36V. If a voltage exceeding 36V is applied to the human body, it can cause injury. This is a safety consideration that engineers take into account when developing circuit projects. To enhance the safety of circuits, engineers typically use an earth ground wire (EGND) in projects involving high voltage and high current, such as household appliances like electric fans, refrigerators, and televisions.
Why do household appliance outlets have three terminal connections? While 220V AC power only requires a live wire and a neutral wire, why are there three terminal connections in the outlets? Among the three terminal connections in the outlet, two are for the live wire and the neutral wire for the 220V power, while the third terminal serves as a protective earth ground (EGND).
It is important to note that the earth ground wire (EGND) is simply connected to the Earth and serves as a protective measure against high voltages. It does not participate in the functionality of the circuit and is independent of the circuit's operation.
Therefore, the earth ground wire (EGND) has a distinct electrical significance and differs from other types of ground wires (GND).
ALSO READ: How To Measure Ground Resistance?
What is GND in circuit

GND in a circuit represents ground, also known as the reference point or system ground. It is typically the connection point that ties other components in the circuit to a common ground potential, forming an integral part of the circuit. Ground potential serves as an electrical reference point, with its potential being considered zero relative to other potentials in the circuit. It can be a low potential relative to the ground or the power supply within the circuit.
Ground serves several important functions in a circuit. Firstly, it provides a stable reference potential, allowing signals in the circuit to be measured and analyzed relative to the ground. Secondly, ground provides a path for current flow, enabling the circuit to operate properly. Additionally, ground can be used to shield the circuit from interference signals, preventing them from affecting the circuit's operation.
In circuit design, the proper use of ground is crucial. Good grounding design can enhance circuit performance and stability. By designing ground points and connections appropriately, interference in the circuit can be minimized, and signal quality can be improved. Furthermore, a well-designed ground system ensures circuit safety.
In case of a fault, ground provides a short-circuit path for current to safely dissipate, thereby avoiding hazards.
There are several common grounding techniques in practical circuit design. Single-point grounding is the most commonly used method, where all ground points are connected to a common grounding point. This approach is suitable for small circuits or simple electronic devices. Distributed grounding is another common technique where ground points from different modules or systems are interconnected to form a grounding network. This approach is suitable for complex systems or large circuit boards. Additionally, there are other grounding methods such as star grounding and loop grounding, which can be chosen based on specific application requirements.
Apart from grounding in circuit design, we often hear terms like "grounding wire" or "lightning protection grounding." These are safety measures related to the concept of circuit grounding.
A grounding wire refers to an earth connection that connects electronic devices or buildings to the ground, aiming to prevent issues like lightning strikes and static accumulation. Lightning protection grounding involves using specialized grounding systems to direct lightning currents safely into the ground, protecting equipment and ensuring personal safety.
In conclusion, GND in a circuit represents "ground" or "grounding" and is an essential concept in electronic circuits. Proper use of ground can enhance circuit performance, stability, and safety.