I have a confession to make: I like heat sinks. Why? It’s hard to say with certainty, but I think it’s a combination of reasons: They have one job (to pull heat away from a source); they’re visible and tangible; they don’t require software or initialization; they’re reliable; they’re consistent, and they don’t push back. They just sit quietly on top of (or next to) a transistor, integrated circuit (IC), or module and do their jobs as defined by their size, geometry, material, and placement, all guided by the basic principles of physics. I even have a modest collection of heat sinks I’ve accumulated along the way (Figures 1, 2, and 3), and there are many that I simply let go by.
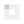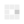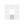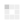
Figure 1: This simple, stamped-metal heat sink mounts on a small metal transistor as a pair of “wings.” (Source: Author).jpg)
Figure 2: This anodized heat sink was designed specifically for the Intel Pentium II processor and includes metal clips that snap the heat sink onto the device. (Source: Author).jpg)
Figure 3: A larger, finned heat sink is designed to cool one or two power devices that are housed in standard TO-3 packages. (Source: Author)
Of course, “heat sink” is a term casually tossed about by many electrical engineers, especially when the real job of forcing heat out to keep things adequately cool becomes the responsibility of mechanical or packaging engineers. That’s unfortunate because a heat sink is a “sink” (but only from one perspective). As it pulls heat away from the source, it must get rid of that heat, so it then becomes a heat “source.” In other words, one person’s sink is another person’s source.
What bothers me is when designers talk about using a heat sink to cool a component and then talk as if the problem of excess heat has gone away. Sorry, but it doesn’t work like that. Under the immutable laws of thermodynamics, heat only flows from a warmer area to a cooler one. If you don't take steps to remove the heat from a heat sink attached to your device by using convection, a heat pipe, forced air, or liquid, then it will linger and eventually create a backup-effect, similar to a pile of vehicles on an accident-blocked road. Both your device and its heat sink will just get hotter and hotter and reach thermal equilibrium at a higher temperature.
Many of today’s ICs are designed to eliminate the need for a heat sink attachment; this is possible when the overall system's thermal situation is designed right. The keyword here is “right.” These devices have a thermal pad underneath their package or use their leads to conduct heat towards the PC board copper. From there, the heat flows to larger copper areas, sometimes using special plated-through-hole vias between the layers of the board.
However, this presents two problems: First, the thermal impedance of the narrow IC leads and the vias is high, so the heat flow is constricted. But let’s assume that the thermal modeling says it will be okay, and let’s move on to the next problem: What other components in the area are also assuming that they can push their heat into that same copper plane? I’ve seen designs where relatively hot ICs and passives were crowded next to each other yet with each assuming it had plenty of square inches of PC copper to use for personal heat-dumping ground.
Sorry! It doesn’t work that way. If the cumulative heat that’s pushed onto the copper creates a temperature close to or, perhaps, above what your components are putting out, then that heat will have nowhere to go. Sometimes the mindset of designers appears to be that they’re all standing in a circle, pointing to the person to their right, saying, “I’m passing my excess heat over to this person.” We all know such thinking doesn’t end well.
The real point is: Heat sinks are wonderful, but they don’t work in a vacuum (“pun” intended—they don’t work well in a real vacuum, as there is no convection, so they would have to rely on conduction alone). Any heat sink must undergo an evaluation to consider both the directional flow of the heat it expels (if the temperature differential is sufficient) and other sources that may be using the same cooling zone to expel excess heat. Ultimately, a heat sink can only do its job when you provide proper accommodations for it to release its heat, which thereby enables it to protect your device.